Vitamin B12
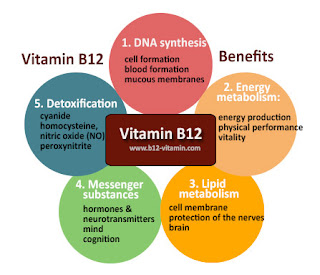
Vitamin B12 is medically called cobalamin, a water-soluble vitamin, which is involved in many important functions for the health
and safety of the body: production of red blood cells, and metabolism.
Metabolism in cells, nerve functions, and DNA or DNA production. Vitamin B12 is
supplied by the body through ingested food. The body is unable to manufacture
it, but it is able to store vitamin B12 for a period of time that may exceed
several years, usually, People get enough vitamin B12 Some people may be more
susceptible to vitamin B12 deficiencies, such as people who have a vegetarian
diet and the elderly. The recommended intake of vitamin B12 is about 2.4
micrograms of vitamin B12. Daily.
Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency
In fact, many people may not notice vitamin B12
deficiency, as the symptoms and associated signs, maybe similar to the
deficiency of many other vitamins and nutrients and the symptoms can be
delayed for several years before they appear.
Symptoms and signs associated
with vitamin B12 deficiency:
Pale and yellowing of the skin: People with vitamin B12
deficiency usually suffer from skin tilts and the white area of the eye to
yellow; this is because vitamin B12 deficiency causes the body's ability to
produce red blood cells.
Fatigue: Reduced production of
erythrocytes lead to a decrease in the ability of these cells to transport
oxygen to all parts of the body, and thus lack of oxygen in the body's cells,
which leads to the feeling of fatigue and fatigue.
Vitamin B12 helps the body produce myelin, which is
important for the functioning of the nervous system (Nervous System), which
protects the nerves of the body, and long-term vitamin B12 deficiency can lead
to nerve damage.Thus feeling numb or numb. Neurological damage caused by vitamin B12 deficiency
can lead to impaired mobility and balance problems, making it more susceptible.
This symptom is common in older adults with vitamin B12 deficiency.
Glossitis:
Studies have shown that glossitis may be the first symptom of people with
vitamin B12 deficiency, as well as other symptoms on the mouth: sores, numbness
of the tongue, and burning sensation in the mouth.
Difficulty in breathing The lack of oxygen in the
body's cells, resulting from low blood levels due to vitamin B12 deficiency,
makes people with dizziness and difficulty breathing, especially in stressful
activities.
Observing changes in the vision: The patient may have
difficulty seeing if the neurological imbalance caused by vitamin B12
deficiency causes problems in the optic nerve extending to the eye.
Mood change: The most common form of
depression, as well as disorders associated with brain dysfunction such as
dementia.
Causes of vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency causes a type of anemia known
as megaloblastic anemia, as the abnormality in the production of red blood
cells lead to abnormal production. In general, vitamin B12 deficiency can be
due to the lack of intrinsic factor to absorb it, or the removal of the vitamin
B12 absorption from the small intestine. Pernicious Anemia, an autoimmune disorder in which
immune system cells attack the cells responsible for the production of the
internal factor in the stomach, the protein responsible for the absorption of
vitamin B12 in the body, leading to Malignant anemia is usually more common in
the case of a family history of infection, in women older than 60 years, and
people with other immune diseases are more susceptible to infection.
Vitamin B12-poor diet: Vitamin B12 deficiency
can be caused by a diet that does not contain vitamin-rich nutrients, but
symptoms and complications are usually delayed in this case; the body can store
its vitamin B12 needs for 2-4 years.
Stomach disorders: Chronic gastritis and gastrectomy
(Gastrectomy).
Intestines Some Crohn's Disease, which causes
inflammation in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract may lead to a decrease in the amount of vitamin B12 that the body can absorb.
Some drugs: The most important proton pump
inhibitors (English: Proton Pump Inhibitors); It works to hinder the body's
production of stomach acid responsible for the extraction of vitamin B12 from
the food intake.
Treatment
of vitamin B12 deficiency
Treatment for anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency
usually begins with oral injections of vitamin B12 or high doses of vitamin
B12. Fortified cereals are generally recommended for elderly people at risk of
vitamin B12 deficiency or vitamin B12 supplements or fortified foods.












Comments